반응형
BeanFactory & ApplicationContext
- xyz.itwill04.bean(패키지)
- CreateBean(클래스) // CreateBeanApp(클래스) //
- InitDestroyMethodBean(클래스) // BeanAttributeApp(클래스)
- LazyInitBean(클래스)
- FactoryMethodBean(클래스)
- DependsOnOneBean(클래스) // DependsOnTwoBean(클래스)
- ScopeBean(클래스)
- 04-1_beanCreate.xml // 04-2_beanAttribute.xml
- 스프링 컨테이너 역할 하는 두가지
→ Bean Factory : 실행시 객체 생성
→ ApplicationContext : ApplicationContext 객체가 초기화 될 때 미리 객체 생성

- BeanFactory 인터페이스를 상속받은 자식클래스로 객체 생성 - BeanFactory 객체
→ BeanFactory 객체를 생성할 때 환경설정파일(Spring Bean Configuration File)을 제공받아 BeanFactory 객체 초기화 처리
→ BeanFactory 객체는 환경설정파일에 등록된 클래스로 미리 객체를 생성하지 않고 객체 제공을 요청할 경우에 객체를 생성하여 제공 - BeanFactory.getBean(String beanName) : 매개변수로 Spring Bean를 구분하기 위한 식별자(beanName)을 전달받아 스프링 컨테이너로부터 객체(Spring Bean)를 생성하여 반환하는 메소드
→ Object 타입의 객체를 반환하므로 반드시 명시적 객체 형변환 사용
→ 매개변수로 전달받은 식별자(beanName)가 없는 경우 NoSuchBeanDefinitionException 발생 - ApplicationContext 인터페이스를 상속받은 자식클래스로 객체 생성 - ApplicationContext 객체
→ ApplicationContext 객체를 생성할 때 환경설정파일(Spring Bean Configuration File)을 제공받아 ApplicationContext 객체 초기화 처리
→ ApplicationContext 객체는 환경설정파일에 등록된 클래스로 미리 객체 생성 - ApplicationContext.getBean(String beanName) : 매개변수로 Spring Bean를 구분하기 위한 식별자(beanName)을 전달받아 스프링 컨테이너로부터 객체(Spring Bean)를 제공받아 반환하는 메소드
→ Object 타입의 객체를 반환하므로 반드시 명시적 객체 형변환 사용
→ 매개변수로 전달받은 식별자(beanName)가 없는 경우 NoSuchBeanDefinitionException 발생 - DL(Dependency Lookup) : 스프링 컨테이너가 관리하는 객체(Spring Bean)을 검색하여 제공하는 기능
- CreateBean(클래스) // CreateBeanApp(클래스)
CreateBean(클래스)
public class CreateBean {
public CreateBean() {
System.out.println("### CreateBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 ###");
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("*** CreateBean 클래스의 display() 메소드 호출 ***");
}
}
CreateBeanApp(클래스)
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public class CreateBeanApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 기존방법
CreateBean bean=new CreateBean();
bean.display();
*/
System.out.println("1.BeanFactory 객체를 생성하여 스프링 컨테이너로 사용하는 방법");
System.out.println("=============== Spring Container 초기화 전 ===============");
//BeanFactory 인터페이스를 상속받은 자식클래스로 객체 생성 - BeanFactory 객체
// => BeanFactory 객체를 생성할 때 환경설정파일(Spring Bean Configuration File)을 제공받아
//BeanFactory 객체 초기화 처리
// => BeanFactory 객체는 환경설정파일에 등록된 클래스로 미리 객체를 생성하지 않고
//객체 제공을 요청할 경우에 객체를 생성하여 제공
BeanFactory factory=new XmlBeanFactory(new FileSystemResource("src/main/resources/04-1_beanCreate.xml"));
System.out.println("=============== Spring Container 초기화 후 ===============");
//BeanFactory.getBean(String beanName) : 매개변수로 Spring Bean를 구분하기 위한 식별자
//(beanName)을 전달받아 스프링 컨테이너로부터 객체(Spring Bean)를 생성하여 반환하는 메소드
// => Object 타입의 객체를 반환하므로 반드시 명시적 객체 형변환 사용
// => 매개변수로 전달받은 식별자(beanName)가 없는 경우 NoSuchBeanDefinitionException 발생
CreateBean bean1=(CreateBean)factory.getBean("createBean");
bean1.display();
System.out.println("===================================================");
System.out.println("2.ApplicationContext 객체를 생성하여 스프링 컨테이너로 사용하는 방법");
System.out.println("=============== Spring Container 초기화 전 ===============");
//ApplicationContext 인터페이스를 상속받은 자식클래스로 객체 생성 - ApplicationContext 객체
// => ApplicationContext 객체를 생성할 때 환경설정파일(Spring Bean Configuration File)을 제공받아
//ApplicationContext 객체 초기화 처리
// => ApplicationContext 객체는 환경설정파일에 등록된 클래스로 미리 객체 생성
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("04-1_beanCreate.xml");
System.out.println("=============== Spring Container 초기화 후 ===============");
//ApplicationContext.getBean(String beanName) : 매개변수로 Spring Bean를 구분하기 위한 식별자
//(beanName)을 전달받아 스프링 컨테이너로부터 객체(Spring Bean)를 제공받아 반환하는 메소드
// => Object 타입의 객체를 반환하므로 반드시 명시적 객체 형변환 사용
// => 매개변수로 전달받은 식별자(beanName)가 없는 경우 NoSuchBeanDefinitionException 발생
//DL(Dependency Lookup) : 스프링 컨테이너가 관리하는 객체(Spring Bean)을 검색하여 제공하는 기능
CreateBean bean2=(CreateBean)context.getBean("createBean");
bean2.display();
System.out.println("================================================");
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)context).close();
}
}
| 1.BeanFactory 객체를 생성하여 스프링 컨테이너로 사용하는 방법 ================ Spring Container 초기화 전 ================ ================ Spring Container 초기화 후 ================ ### CreateBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 ### *** CreateBean 클래스의 display() 메소드 호출 *** 실행시 객체를 생성한다(Spring Container 초기화 이후 객체생성) |
| 2. ApplicationContext 객체를 생성하여 스프링 컨테이너로 사용하는 방법 ================ Spring Container 초기화 전 ================ ### CreateBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 ### ================ Spring Container 초기화 후 ================ *** CreateBean 클래스의 display() 메소드 호출 *** 미리 객체를 생성하고 필요한걸 가져다 쓴다(Spring Container 초기화 전,후 사이에 객체생성) |

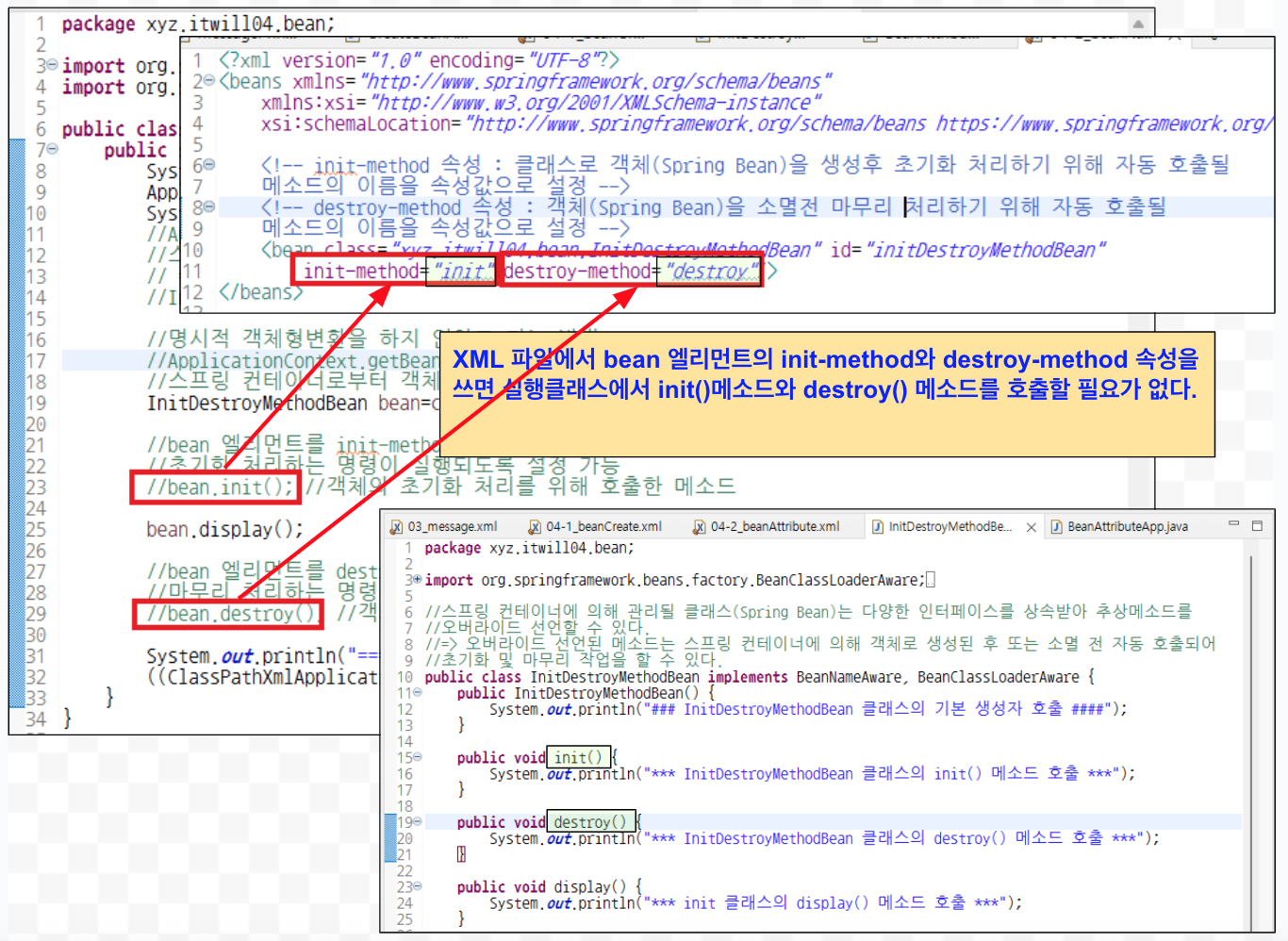
Bean 엘리먼트 속성
속성내용
| id / name |
|
| init-method | 클래스로 객체(Spring Bean)을 생성후 초기화 처리하기 위해 자동 호출될 메소드의 이름을 속성값으로 설정 |
| destroy-method | destroy-method 속성 : 객체(Spring Bean)을 소멸전 마무리 처리하기 위해 자동 호출될 메소드의 이름을 속성값으로 설정 |
| factory-method | 싱글톤 클래스에서 객체를 반환하는 메소드의 이름을 속성값으로 설정 → 정적영역의 명령으로 객체를 생성하여 스프링 컨테이너에 의해 관리된다 |
| lazy-init |
|
| depends-on |
|
init-method / destroy-method 속성
BeanAttributeApp(클래스)
public class BeanAttributeApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=============== Spring Container 초기화 전 ===============");
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("04-2_beanAttribute.xml");
System.out.println("=============== Spring Container 초기화 후 ===============");
//ApplicationContext.getBean(String beanName) : 매개변수로 식별자(beanName)를 전달받아
//스프링 컨테이너로부터 객체(Spring Bean)를 제공받아 반환하는 메소드
// => Object 타입의 객체를 반환하므로 반드시 명시적 객체 형변환 사용
//InitDestroyMethodBean bean=(InitDestroyMethodBean)context.getBean("initDestroyMethodBean");
//명시적 객체형변환을 하지 않아도 되는 방법
//ApplicationContext.getBean(String beanName, Class<T> class) : 매개변수로 식별자(beanName)를 전달받아
//스프링 컨테이너로부터 객체(Spring Bean)를 제공받아 객체 형변환하여 반환하는 메소드
InitDestroyMethodBean bean=context.getBean("initDestroyMethodBean", InitDestroyMethodBean.class);
//bean 엘리먼트를 init-method 속성을 사용해 객체가 생성된 후에 메소드가 자동 호출되어
//초기화 처리하는 명령이 실행되도록 설정 가능
//bean.init(); //객체의 초기화 처리를 위해 호출한 메소드
bean.display();
//bean 엘리먼트를 destroy-method 속성을 사용해 객체가 소멸되기 전에 메소드가 자동 호출되어
//마무리 처리하는 명령이 실행되도록 설정 가능
//bean.destroy(); //객체의 마무리 처리를 위해 호출한 메소드| =============== Spring Container 초기화 전 =============== ### InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### =============== Spring Container 초기화 후 =============== *** InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 init() 메소드 호출 *** *** InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 display() 메소드 호출 *** *** InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 destroy() 메소드 호출 *** ========================================================= |
04-2_beanAttribute.xml
<!-- init-method 속성 : 클래스로 객체(Spring Bean)을 생성후 초기화 처리하기 위해 자동 호출될
메소드의 이름을 속성값으로 설정 -->
<!-- destroy-method 속성 : 객체(Spring Bean)을 소멸전 마무리 처리하기 위해 자동 호출될
메소드의 이름을 속성값으로 설정 -->
<bean class="xyz.itwill04.bean.InitDestroyMethodBean" id="initDestroyMethodBean"
init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"/>| =============== Spring Container 초기화 전 =============== ### InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### *** InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 init() 메소드 호출 *** =============== Spring Container 초기화 후 =============== *** InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 display() 메소드 호출 *** ========================================================= *** InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 destroy() 메소드 호출 *** |
- aware 인터페이스가 11개가 있는데, 특별한 경우에만 사용될 일이 있다.
(초기화 작업을 위해 사용하는 인터페이스라고 생각하면 된다.)
lazy-init 속성
- LazyInitBean(클래스)
- 스프링 컨테이너 역할을 하는 두 가지(Bean Factory // ApplicationContext)가 있다.
→ Bean Factory : 실행시(getBean) 객체 생성
→ ApplicationContext : ApplicationContext 객체가 초기화 될 때 미리 객체 생성 - 이 두개 중 우리는 ApplicationContext 를 사용하는데, ApplicationContext 의 경우 ApplicationContext 객체가 초기화 될때 미리 객체가 생성된다.
- 그런데 이 Bean 엘리먼트의 lazy-init 속성에 true를 주면 스프링 컨테이너가 초기화될 때 객체를 미리 생성하지 않고 getBean() 메소드를 호출할때 객체를 생성하여 제공한다.
|
| lazy-init (false) |
=============== Spring Container 초기화 전 =============== ### LazyInitBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### =============== Spring Container 초기화 후 =============== *** init 클래스의 display() 메소드 호출 *** ========================================================= |
| lazy-init (true) |
=============== Spring Container 초기화 전 =============== =============== Spring Container 초기화 후 =============== *** init 클래스의 display() 메소드 호출 *** ========================================================= ### LazyInitBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### ========================================================= |
factory-method 속성
- 스프링 컨테이너는 환경설정파일에 등록된 모든 클래스를 리플렉션 기술을 사용해 객체를 미리 생성하여 관리한다
→ 리플렉션 기술은 명령 실행시 객체를 생성하며 접근 제한자에 상관없는 필드 또는 메소드를 사용할 수 있다.
→ 생성자가 은닉화 선언되어 있어도 스프링 컨테이너는 생성자로 객체 생성 가능 - 문제점 : 환경설정파일에 싱글톤 클래스를 등록하여 해당 클래스를 Class 객체로 생성한 후 정적 영역의 명령으로 객체를 생성한 후 스프링 컨테이너에 의해 객체를 다시 생성한다.
→ 싱글톤 클래스로 객체가 2개 생성된다. - 해결법 : bean 엘리먼트에 factory-method 속성을 사용해 객체가 하나만 생성되도록 설정
- factory-method 속성 : 싱글톤 클래스에서 객체를 반환하는 메소드의 이름을 속성값으로 설정
→ 정적영역의 명령으로 객체를 생성하여 스프링 컨테이너에 의해 관리된다
| =============== Spring Container 초기화 전 =============== ### InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### *** InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 setBeanName() 메소드 호출 *** *** InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 setBeanClassLoader() 메소드 호출 *** *** InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 init() 메소드 호출 *** ### FactoryMethodBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### ### FactoryMethodBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### =============== Spring Container 초기화 후 =============== *** init 클래스의 display() 메소드 호출 *** ========================================================= ### LazyInitBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### ========================================================= *** InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 destroy() 메소드 호출 *** 싱글톤 클래스로 적용했는데 생성자가 두번 호출되서 객체가 두개가 만들어진다. 왜? 하나는 static에서 하나가 만들어지고, 또 다른 하나는 Spring Container에서 만들어지는 것이다. |
depends-on 속성
- DependsOnOneBean(클래스) // DependsOnTwoBean(클래스)
- 스프링 컨테이너는 bean 엘리먼트 작성 순서대로 읽어 클래스를 객체로 생성
- depends-on 속성 : bean 엘리먼트의 식별자(beanName)를 속성값으로 설정
→ bean 엘리먼트의 클래스로 객체를 생성하기 전에 depends-on 속성값으로 설정된 beanName의 클래스로 객체를 먼저 생성
04-2_beanAttribute.xml (depends-on 속성 적용 전)
<bean class="xyz.itwill04.bean.DependsOnOneBean"/>
<bean class="xyz.itwill04.bean.DependsOnTwoBean"/>| ### DependsOnOneBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### ### DependsOnTwoBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### |
04-2_beanAttribute.xml (depends-on 속성 적용 후)
<bean class="xyz.itwill04.bean.DependsOnOneBean" depends-on="dependsOnTwoBean"/>
<bean class="xyz.itwill04.bean.DependsOnTwoBean" id="dependsOnTwoBean"/>| ### DependsOnTwoBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### ### DependsOnOneBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### |
scope 속성
- scope 속성 : singleton(기본값), prototype, request, session 중 하나를 속성값으로 설정
- singleton 또는 prototype : 객체의 생성 갯수를 설정하는 속성값
→ singleton 속성값 : 스프링 컨테이너가 bean 엘리먼트의 클래스로 객체를 하나만 생성하여 제공
→ prototype 속성값 : 스프링 컨테이너가 bean 엘리먼트의 클래스로 객체를 여러개 생성하여 제공 - request 또는 session : 웹프로그램 작성시 객체의 사용범위를 설정하는 속성값
- scope 속성값을 [prototype]으로 설정하면 lazy-init 속성값이 자동으로 [true]로 설정된다.
→ 스프링 컨테이너가 초기화 될 때 객체를 미리 생성하지 않고 getBean() 메소드 호출시 생성
- ScopeBean(클래스)
| 04-2_beanAttribute.xml (depends-on 속성 적용 후) |
| context.getBean("lazyInitBean", LazyInitBean.class); System.out.println("=============================================="); ScopeBean bean1=context.getBean("singletonBean", ScopeBean.class); ScopeBean bean2=context.getBean("singletonBean", ScopeBean.class); ScopeBean bean3=context.getBean("singletonBean", ScopeBean.class); |
| <bean class="xyz.itwill04.bean.ScopeBean" id="singletonBean" lazy-init="true" scope="singleton"/> =============== Spring Container 초기화 후 =============== *** init 클래스의 display() 메소드 호출 *** ========================================================= ### LazyInitBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### ========================================================= ### ScopeBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### bean1 = xyz.itwill04.bean.ScopeBean@53aac487 bean2 = xyz.itwill04.bean.ScopeBean@53aac487 bean3 = xyz.itwill04.bean.ScopeBean@53aac487 ========================================================= *** InitDestroyMethodBean 클래스의 destroy() 메소드 호출 *** getBean이 세번 호출됐지만 생성자로 객체는 하나만 만든다. 두번째, 세번째 호출에서는 첫번째 만들어진 객체로 사용한다. 그 이유는 bean엘리먼트에 scope 속성이 있는데 그 속성값이 singleton으로 되어있기 때문이다 ⇒ 그래서 DAO 클래스나 service 클래스를 싱글톤 클래스로 작성할 필요가 없다. |
| <bean class="xyz.itwill04.bean.ScopeBean" id="prototypeBean" scope="prototype"/> ### ScopeBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### ### ScopeBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### ### ScopeBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 #### bean4 = xyz.itwill04.bean.ScopeBean@52b1beb6 bean5 = xyz.itwill04.bean.ScopeBean@273e7444 bean6 = xyz.itwill04.bean.ScopeBean@7db12bb6 scope속성값이 prototype인 경우 getBean으로 여러번 호출시 객체도 여러개 생성된다. |
XML에서 Bean 엘리먼트를 쓰는게 아니라 어노테이션으로 사용하는 방법(스프링 부트 방법)
- 스프링 부트에는 XML를 전혀 사용하지 않기 때문에 이 어노테이션 방법을 사용해야 한다.
- component-scan : 스프링 컨테이너가 클래스에서 사용된 스프링 어노테이션을 검색해 처리할 수 있도록 설정하는 엘리먼트
- base-package 속성 : 스프링 어노테이션을 사용한 클래스가 작성된 패키지를 속성값으로 설정
→ 상위 패키지를 속성값으로 설정하면 하위 패키지도 자동으로 포함
| 04-3_beanAnnotaion.xml |
| <!-- <bean class="xyz.itwill04.bean.AnnotationBean" id="annotationBean"></bean> --> <!-- component-scan : 스프링 컨테이너가 클래스에서 사용된 스프링 어노테이션을 검색해 처리할 수 있도록 설정하는 엘리먼트 --> <!-- base-package 속성 : 스프링 어노테이션을 사용한 클래스가 작성된 패키지를 속성값으로 설정 --> <!-- => 상위 패키지를 속성값으로 설정하면 하위 패키지도 자동으로 포함 --> <context:component-scan base-package="xyz.itwill04.bean"></context:component-scan> 예를들어 base-package="xyz" ⇒ xyz 패키지 하위에 있는 스프링 어노테이션 검색하여 처리 base-package="xyz.itwill04" ⇒ xyz.itwill04 패키지 하위에 있는 스프링 어노테이션 검색하여 처리 base-package="xyz.itwill04.bean" ⇒ xyz.itwill04.bean 패키지 하위에 있는 스프링 어노테이션 검색하여 처리 가독성을 좋게 하기 위해서는 구체적으로 범위를 좁혀서 적어주는게 좋다. |
- AnnotationBean(클래스) // AnnotationBeanApp(클래스)
- AnnotationConfigurationBean(클래스) // ComponentAnnotationBean(클래스) // ComponentAnnotationBeanApp(클래스)
- 04-3_beanAnnotaion.xml
- 어노테이션을 사용하기 위해서는 XML 환경설정 파일에서 component-scan 엘리먼트를 사용해야 하는데, 자동완성을 확인해보면 component-scan 엘리먼트는 보이지 않는다.
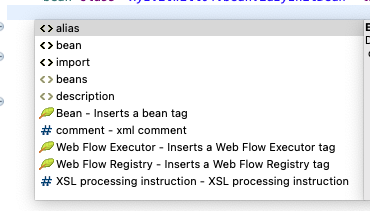
- component-scan 엘리먼트는 Spring Beans 스키마 파일에 없고 Spring Context 스키마 파일에 있어서 XML 파일을 만들때 Configure Namespaces에서 beans 스키마 말고도 context 스키마에 있는 spring-context에도 체크를 해줘야 한다.
만약 체크를 하지 못하고 파일을 이미 만들었을 경우, 지웠다가 다시 만드는게 아니라 코드 적는 뷰 영역 하단 source 탭 옆에 Namespaces 탭이 있는데 거기서 추가로 체크를 할 수 있다. - XML파일에서 component-scan 엘리먼트
→ 근데 처음에는 자동완성에 component-scan 엘리먼트가 안보인다.
→ 이건 Spring Context 스키마 파일에 있다.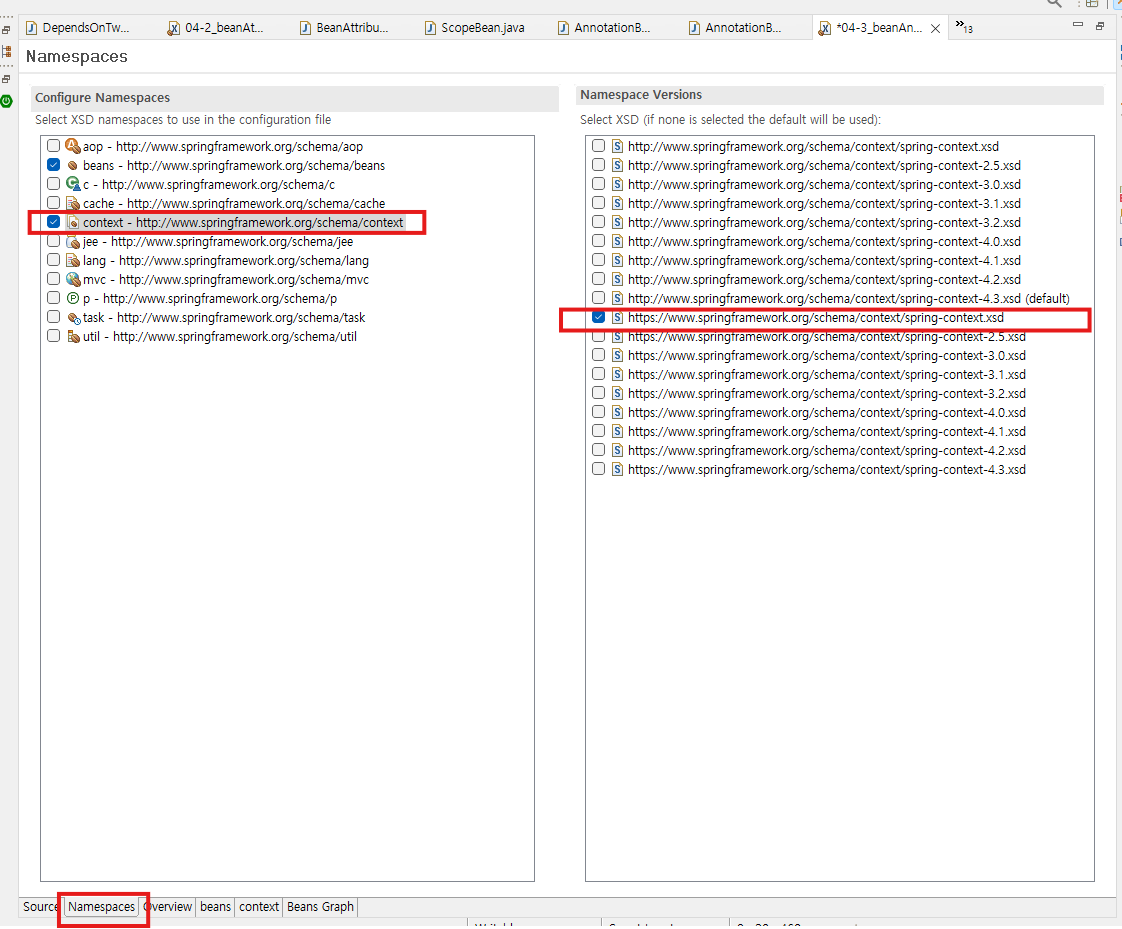
- 클래스를 환경설정 파일로 만드는거라고 생각하면 된다.

- 스프링은 XML파일에 Bean 엘리먼트를 쓰는게 더 편하고 효율적이다.
어노테이션 방법은 나중에 스프링 부트에서 써야하는 방법이기 때문에 미리 알아본 것이다. - 객체반환하는 configuration 클래스에 어노테이션을 써서 할수도 있지만,
- 클래스에 @Component 어노테이션만 써서 할 수도 있다. ⇒ 클래스를 만들때 Spring Bean으로 등록하고 싶을때 쓰는 방법. 배포된 클래스에는 쓸 수 없고 우리가 작성한 클래스에만 쓸 수 있다.
- 그런데 @Component 어노테이션보다는 얘를 상속받은 다른 어노테이션을 더 많이 쓰기는 한다.
기존에 썼던 XML 방법
AnnotationBean(클래스)
public class AnnotationBean {
public AnnotationBean() {
System.out.println("### AnnotationBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 ####");
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("*** AnnotationBean 클래스의 display() 메소드 호출 ***");
}
}
04-3_beanAnnotaion.xml
<bean class="xyz.itwill04.bean.AnnotationBean" id="annotationBean"/>
AnnotationBeanApp(클래스)
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=============== Spring Container 초기화 전 ===============");
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("04-3_beanAnnotaion.xml");
System.out.println("=============== Spring Container 초기화 후 ===============");
AnnotationBean bean=context.getBean("annotationBean", AnnotationBean.class);
bean.display();
System.out.println("=======================================================");
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)context).close();
}
- 빈 엘리먼트를 쓰지 않아도 어노테이션을 사용해 클래스를 Spring Bean으로 등록할 수 있다.
어노테이션 사용 방법
AnnotationBean(클래스)
public class AnnotationBean {
public AnnotationBean() {
System.out.println("### AnnotationBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 ####");
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("*** AnnotationBean 클래스의 display() 메소드 호출 ***");
}
}
AnnotationConfigurationBean(클래스) - 어노테이션
//@Configuration : 스프링 컨테이너에 의해 관리될 객체를 생성하여 제공하는 기능의 클래스로
//등록하기 위한 어노테이션
//=> Spring Bean Configuration File과 유사한 기능을 제공하는 어노테이션
(Bean Configuration File 과 같은 기능을 하는 클래스가 되는거라 생각하면 된다)
@Configuration
public class AnnotationConfigurationBean {
//@Bean : 스프링 컨테이너에 의해 관리될 객체를 생성하여 반환하는 메소드를 등록하기 위한 어노테이션
//=> Spring Bean Configuration File의 bean 엘리먼트와 유사한 기능을 제공하는 어노테이션
//=> 메소드의 이름을 식별자(beanName)으로 사용
//=> @Bean 어노테이션의 name 속성을 사용하면 식별자(beanName) 변경이 가능하다.
@Bean
public AnnotationBean annotationBean() {
return new AnnotationBean();
}
/*
@Bean
public ComponentAnnotationBean componentAnnotationBean() {
return new ComponentAnnotationBean();
}
*/
}
AnnotationBeanApp(클래스)
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=============== Spring Container 초기화 전 ===============");
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("04-3_beanAnnotaion.xml");
System.out.println("=============== Spring Container 초기화 후 ===============");
AnnotationBean bean=context.getBean("annotationBean", AnnotationBean.class);
bean.display();
System.out.println("=======================================================");
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)context).close();
}
| 이 경우 XML 환경설정 파일이 아니라 클래스 파일에서 어노테이션을 사용해 객체를 만들어준다. 그리고 만약 추가적으로 Bean 등록이 필요할 경우 [AnnotationConfigurationBean] 클래스에 @Bean 어노테이션으로 추가해주면 된다. 그런데, 이렇게 객체가 추가될때마다 @Bean 어노테이션을 추가해주는 것도 귀찮을 수 있는데, 그보다 더 편한 방법이 아래와 같다. ⇒ 클래스에 @Component 어노테이션을 추가하는 방법 |
어노테이션 사용 방법(보다 더 편한 방법)
ComponentAnnotationBean(클래스)
//@Component : 클래스를 스프링 컨테이너가 관리하는 Spring Bean으로 객체로 등록하기 위한 어노테이션
//=> 클래스의 이름을 식별자(beanName)로 사용 - 첫번째 문자는 소문자로 변환되어 사용
//@Component 어노테이션의 value 속성을 사용하여 식별자 변경이 가능하다 - value 속성 외에 다른
//속성이 없는 경우 속성값만 설정이 가능하다.
@Component("bean")
public class ComponentAnnotationBean {
public ComponentAnnotationBean() {
System.out.println("### ComponentAnnotationBean 클래스의 기본 생성자 호출 ###");
}
public void display() {
System.out.println("*** ComponentAnnotationBean 클래스의 display() 메소드 호출 ***");
}
}
AnnotationBeanApp(클래스)
public class ComponentAnnotationBeanApp {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("==== Spring Container 초기화 전====");
ApplicationContext context=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("04-3_beanAnnotaion.xml");
System.out.println("==== Spring Container 초기화 후 =====");
//ComponentAnnotationBean bean=context.getBean("componentAnnotationBean", ComponentAnnotationBean.class); ⇒ value속성으로 이름 설정을 따로 하지 않은 경우
ComponentAnnotationBean bean=context.getBean("bean", ComponentAnnotationBean.class); ⇒ value속성으로 이름 설정을 한 경우
bean.display();
System.out.println("=================================================");
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)context).close();
}
}반응형
'IT개발 > Spring Framework' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring IoC(Inversion of Control) - 제어의 역행(스프링/프레임워크/백엔드/개발/프로그래밍) (2) | 2024.12.04 |
|---|---|
| Spring Framework란?(스프링 프레임워크/자바/백엔드개발) (0) | 2024.12.03 |
| Spring IoC(Spring/Spring Boot/Java/IoC/backend/제어의역행/자바/스프링/스프링부트) (0) | 2024.08.30 |
| 스프링 사전설정 - Maven 라이브러리 빌드, 로그구현체 설정(Spring/Java/Framework/백엔드/웹개발/Backend) (0) | 2024.08.29 |
| 스프링 사전설정(Spring/Java/Framework/백엔드/웹개발/Backend) (1) | 2024.08.28 |



댓글